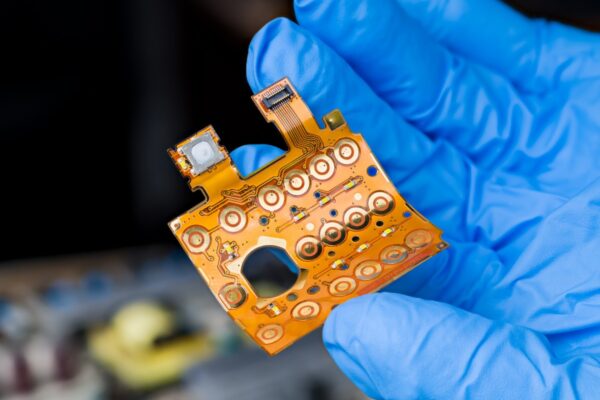
What is Flex PCB (Flexible PCB)
Flex PCB (flexible PCB) is designed to be flexible and capable of bending. It is widely used in various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical applications.
Flex PCBs are composed of multiple layers, typically including a polyimide (PI) base material, an adhesive layer, a copper layer for conducting electrical signals, and a coverlay for protection. In some cases, stiffeners may be added to provide additional support. The metallic layer is usually made of copper and is bonded to a dielectric layer, often made of polyimide. The thickness of the metal layer can vary, as can the dielectric thickness.
One of the key differences between flex PCBs and traditional rigid PCBs is the unique design and fabrication process involved. Designing a flexible circuit requires specific considerations and adherence to design rules, often referred to as “flex-izing.” This specialized design approach ensures that the flex PCB can withstand bending and flexing without compromising its functionality.
Their flexibility allows for more compact and space-saving designs, making them ideal for applications where size and weight are critical factors. The ability to bend and shape the PCB also enables easier installation in tight or irregular spaces. Additionally, flex PCBs are more durable and reliable, as they can withstand mechanical stress and vibrations better than rigid PCBs.