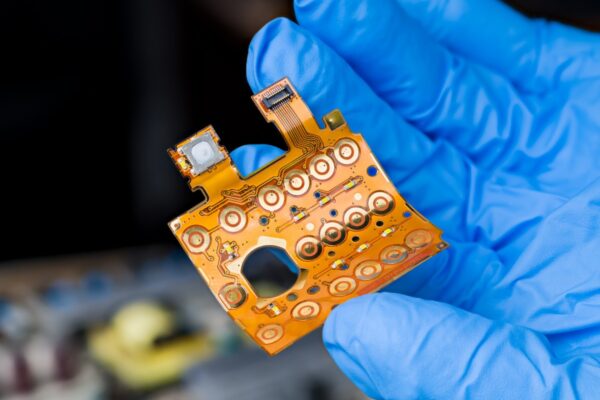
What is Electroconductive Paste Printed Board
An electroconductive paste printed board is manufactured using electroconductive paste. This specialized paste, typically composed of copper, is applied to the PCB to create conductive traces. These traces serve as pathways for electrical current to flow through the board. The electroconductive paste offers several advantages over traditional methods of creating conductive traces on PCBs.
The copper-based pastes, such as those developed by Copprint, exhibit superior electrical properties compared to silver pastes. They offer higher conductivity while being more cost-effective. This makes them an attractive option for creating reliable and efficient conductive traces on PCBs.
In the past, soldering on printed silver traces has been challenging, leading to the use of silver-based electrically conductive adhesives (ECAs) as an alternative. However, the development of copper-based electroconductive pastes has revolutionized the industry. It is now possible to solder components onto traces formed with these pastes using standard solder pastes. This standardized approach simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces costs.
To ensure compatibility between the electroconductive paste and the solder paste, a testing method is employed. Rather than relying on visual inspection, a more accurate method involves soldering small chips to the printed copper traces and measuring the die shear force required to detach the chip. Compatible solder pastes will form a strong bond that is difficult to detach, while non-compatible pastes will not form a bond and can be easily detached.
In addition to PCB board printing, electroconductive paste finds applications in various industries. It is used in the production of membrane switches, RFID tags, and PV cells. The versatility of electroconductive paste allows it to be used on multiple substrates, including FR4, Paper, Glass, PI, PET, and more.